
In the fast-paced world of business transactions, it’s common for errors to arise—overcharges, returns, damaged goods, or discounts applied post-sale. To adjust these discrepancies without disturbing your financial books too drastically, credit notes (also known as credit invoices) come to the rescue. Understanding when and how to issue a credit note is crucial for accurate accounting, regulatory compliance, and customer trust.
In this article, we’ll demystify the concept of credit notes, explain when they should be used, how to issue them properly, and highlight best practices for their management.
What is a Credit Note?
A credit note is a document issued by a seller to a buyer, acknowledging that a certain amount has been credited to the buyer's account. This is typically due to goods being returned, an overcharge, a service cancellation, or a post-invoice discount. Essentially, it acts as a negative invoice and adjusts the amount the buyer owes or has already paid.
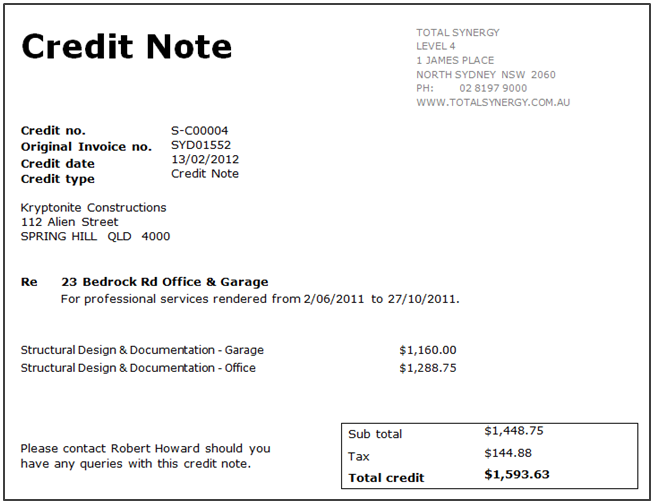
Key Features of a Credit Note:
- Issued by the seller
- Reduces the value of a previously issued invoice
- Includes reference to the original invoice
- Clearly states the reason for the credit
For instance, if a business issues an invoice for Rs10,000 but later realizes that Rs1,000 worth of goods were returned or discounted, a credit note for Rs1,000 will be issued.
Common Scenarios for Issuing a Credit Note
Understanding when to issue a credit note is vital. Below are some typical business scenarios that warrant their use:
- Overbilling or Errors on the Original Invoice: Pricing or quantity errors can be corrected with a credit note.
- Return of Goods: Customers returning goods for various reasons.
- Post-Invoice Discounts: Discounts agreed upon after invoice issuance.
- Service Cancellation or Partial Completion: Adjustment for incomplete services.
- Damaged or Defective Items: Adjustment for faulty goods.
When Should You Use a Credit Note?
- Customer Request or Dispute: To address concerns or errors raised by the customer.
- Audit and Tax Compliance: Issuing within legally prescribed periods helps avoid penalties.
- Correcting Revenue Recognition: Ensures books reflect true revenue figures.
- Inventory Reconciliation: Helps match stock movements with accounting records.
How to Create a Credit Note
Creating a credit note isn't just about subtracting an amount from an invoice. It should be a formal document that includes key elements:
Mandatory Components:
- Title: Clearly labeled as "Credit Note"
- Credit Note Number: Unique and sequential
- Date of Issue
- Customer and Seller Details
- Reference to Original Invoice
- Description of Adjusted Goods/Services
- Reason for Issuance
- Credit Amount
- Authorized Signature
Sample Format:
CREDIT NOTE
Credit Note No: CN-2025/047
Date: 19th July 2025
Original Invoice No: INV-2025/230
Invoice Date: 1st July 2025
Customer: ABC Enterprises
Address: 123 Business Street, Mumbai
Reason: Goods Returned (3 items - Defective)
Description:
- Product X (3 Units Returned)
- Original Price: Rs 3000
- Credit Amount: Rs 3000
Tax Adjustment: Rs 540 (18% GST)
Total Credit: Rs 3,540
Issued By: XYZ Pvt. Ltd.
GSTIN: 27ABCDE1234F1Z6
Authorized Signatory: ______________
Credit Note vs. Refund: What's the Difference?
Though often confused, a credit note is not the same as a refund.
Credit Note:
- Adjusts a future transaction
- Used in B2B relationships
- Reflects adjustments in account balance
Refund:
- Involves returning money to the customer
- Common in B2C sales
- Used when no future transaction is expected
Example: A wholesaler receives a credit note for future purchases, while a consumer gets their money back.
Legal & Accounting Considerations
GST Compliance (India):
- Must reference the original invoice
- Reported in GSTR-1 of the relevant month
- Issued within the permitted time period
VAT Compliance (EU and Others):
Similar documentation and tax adjustment rules apply under VAT laws.
Accounting Entries:
Seller’s Books:
- Debit: Sales Return or Revenue
- Credit: Accounts Receivable
Buyer’s Books:
- Debit: Accounts Payable
- Credit: Purchase Return or Expense Adjustment
Best Practices for Using Credit Notes
- Use accounting software for automation and accuracy
- Maintain a sequential numbering system
- Mention the reason for issuance clearly
- Issue credit notes promptly
- Train accounting and finance staff
- Store records securely for audit trails
Credit notes may seem like a minor part of financial operations, but their role in maintaining accurate books, customer satisfaction, and legal compliance is significant. By understanding when and how to issue them, you not only reduce errors but also build professional credibility with clients.
Whether you’re a small business or a large enterprise, implementing strong credit note practices ensures smoother transactions, better reporting, and trust-building with your partners.
FAQs
Q1: Can a credit note be canceled or reversed?
Yes, if issued in error, it can be canceled through proper documentation or a debit note, depending on local laws.
Q2: Are credit notes taxable?
They adjust the taxable value of an original invoice. Taxes included in the original invoice must be reversed appropriately.
Q3: What if the customer doesn’t accept the credit note?
Clarify the reason and refer to prior agreements. Documentation is essential for dispute resolution and audits.
Tip: Use invoicing tools with built-in credit note features to simplify your workflow and stay compliant.
