In every business transaction, documents play a vital role in ensuring smooth communication between sellers, buyers, and authorities. Among these documents, challan and bill are two terms often misunderstood or used interchangeably. However, they serve entirely different purposes. A clear understanding of the difference between challan and bill is essential for businesses to remain compliant, transparent, and efficient.
This blog will explain what challan and bill mean, their uses, and their differences, with examples to help you understand them better.
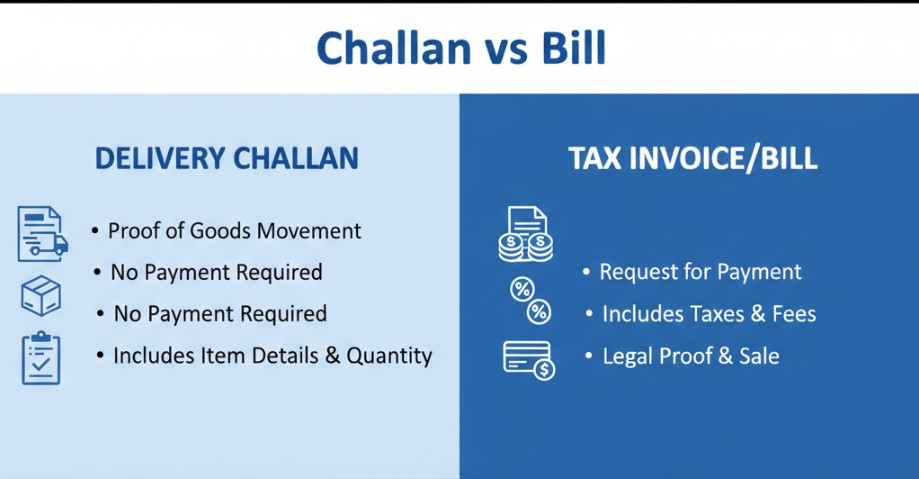
What is a Challan?
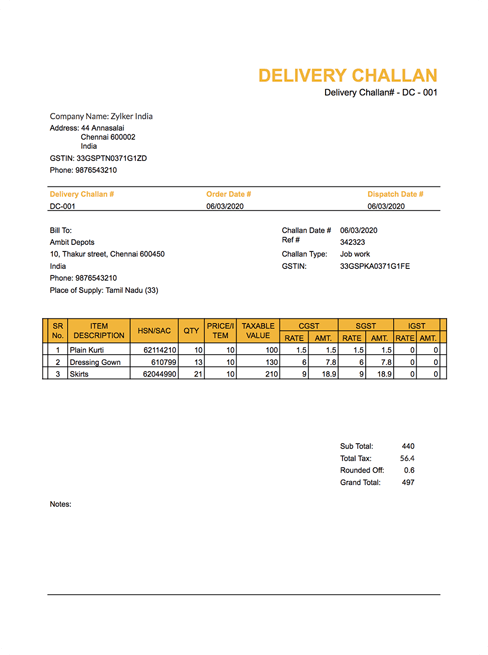
A challan is a document used as proof of delivery, transport, or payment. It does not confirm a sale but instead acts as evidence of goods being moved or taxes being paid.
Types of Challans
- Delivery Challan – Issued when goods are transported without a bill (e.g., sending goods for approval or job work).
- Transport Challan – Used by logistics companies to confirm the movement of goods.
- Payment Challan – Common in taxation (like GST challan, income tax challan), it serves as proof of payment to the government.
Key Features
- Contains challan number, date, quantity, description of goods, sender and receiver details.
- Does not indicate a financial transaction or sale.
- Used widely in goods return, sample dispatch, or tax payments.
Example:
A manufacturer sends raw material to another company for processing. Since it is not a sale, a delivery challan is issued, not a bill.
What is a Bill (Invoice)?
A bill or invoice is a legal document issued by a seller to a buyer, demanding payment for goods or services supplied. Unlike a challan, a bill confirms a sale has taken place.

Key Features
- Includes seller and buyer details, invoice number, date, product/service description, unit price, taxes, and total payable amount.
- Acts as proof of sale and creates a legal obligation for payment.
- Essential for accounting, tax filing, and claiming input tax credit (in GST).
Example:
A shopkeeper sells a washing machine to a customer. A bill/invoice is issued that shows product details, tax charged, and final amount payable.
Key Differences Between Challan and Bill
Here’s a quick comparison to make things crystal clear:
| Aspect | Challan | Bill (Invoice) |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Proof of delivery, transport, or payment | Proof of sale and payment obligation |
| Legal Status | Not a legal proof of sale | Legal proof of a sales transaction |
| Details Included | Challan no., date, goods description, quantity, receiver | Invoice no., date, buyer & seller details, item description, tax, total payable |
| Use in GST/Tax | Delivery challan in specific cases, payment challan for taxes | Mandatory for sales, tax filing, and ITC claims |
| Payment Requirement | No obligation to pay | Creates a payment obligation |
| Example | Sending goods for approval/job work | Selling goods or services |
When to Use a Challan vs. a Bill
- Challan:
- Sending goods for approval or return.
- Transporting materials for job work.
- Making tax payments (GST challan, Income Tax challan).
- Bill (Invoice):
- Selling goods or services.
- Recording transactions in accounts.
- Claiming tax credits or deductions.
Common Misunderstandings
- A delivery challan cannot replace a sales invoice.
- Businesses often wrongly use challans for taxable sales, which may lead to compliance issues.
- Bills are always needed for sales, while challans are supplementary documents.
Why Correct Usage Matters for Businesses
Using challans and bills appropriately helps:
- Maintain compliance with GST and tax laws.
- Avoid penalties during audits.
- Ensure clarity and trust between business partners.
- Keep accurate records for accounting and financial reporting.
Example Scenarios
- Scenario 1: A clothing manufacturer sends fabric to a tailor for stitching → Delivery Challan issued.
- Scenario 2: A retailer sells finished garments to a customer → Bill issued.
- Scenario 3: A business pays its monthly GST liability → GST Payment Challan generated.
Vyaaparkhata – Simplifying Challan and Bill Management
Manually creating and managing challans and bills can be confusing and time-consuming. This is where Vyaaparkhata – Invoice Creation and Management Software makes a huge difference. With Vyaaparkhata, businesses can:
- Create GST-compliant invoices in just a few clicks.
- Generate delivery challans instantly for goods in transit or job work.
- Keep all challans, invoices, and tax-related documents organized in one place.
- Reduce manual errors and save time through automation.
For small businesses and enterprises alike, Vyaaparkhata ensures hassle-free documentation and smooth financial management.
In summary, both challan and bill are important business documents but serve different purposes.
- A challan is used for delivery, transport, or payment confirmation.
- A bill is a legal document that proves a sale and demands payment.
Understanding the difference ensures compliance, transparency, and smooth business operations. And with smart digital solutions like Vyaaparkhata, managing challans and bills has never been easier.
