
A GST Sales Invoice is a document issued by a registered seller to the buyer, serving as legal proof of goods or services supplied. It ensures compliance with GST laws, enables Input Tax Credit (ITC) for buyers, and maintains transparency in business transactions.
- Legal Compliance: Ensures adherence to GST laws.
- Input Tax Credit (ITC): Allows buyers to claim ITC, reducing their tax liability.
- Transparent Transactions: Provides clarity between suppliers and recipients.
We, VyapaarKHATA, help in creating an Invoice within 2 minutes. Our simple and easy Invoice creation helps the business to save their time and manage their records digitally. Our invoice creation application create the invoice in image, pdf formate which can be taken any where in your mobile wallet.
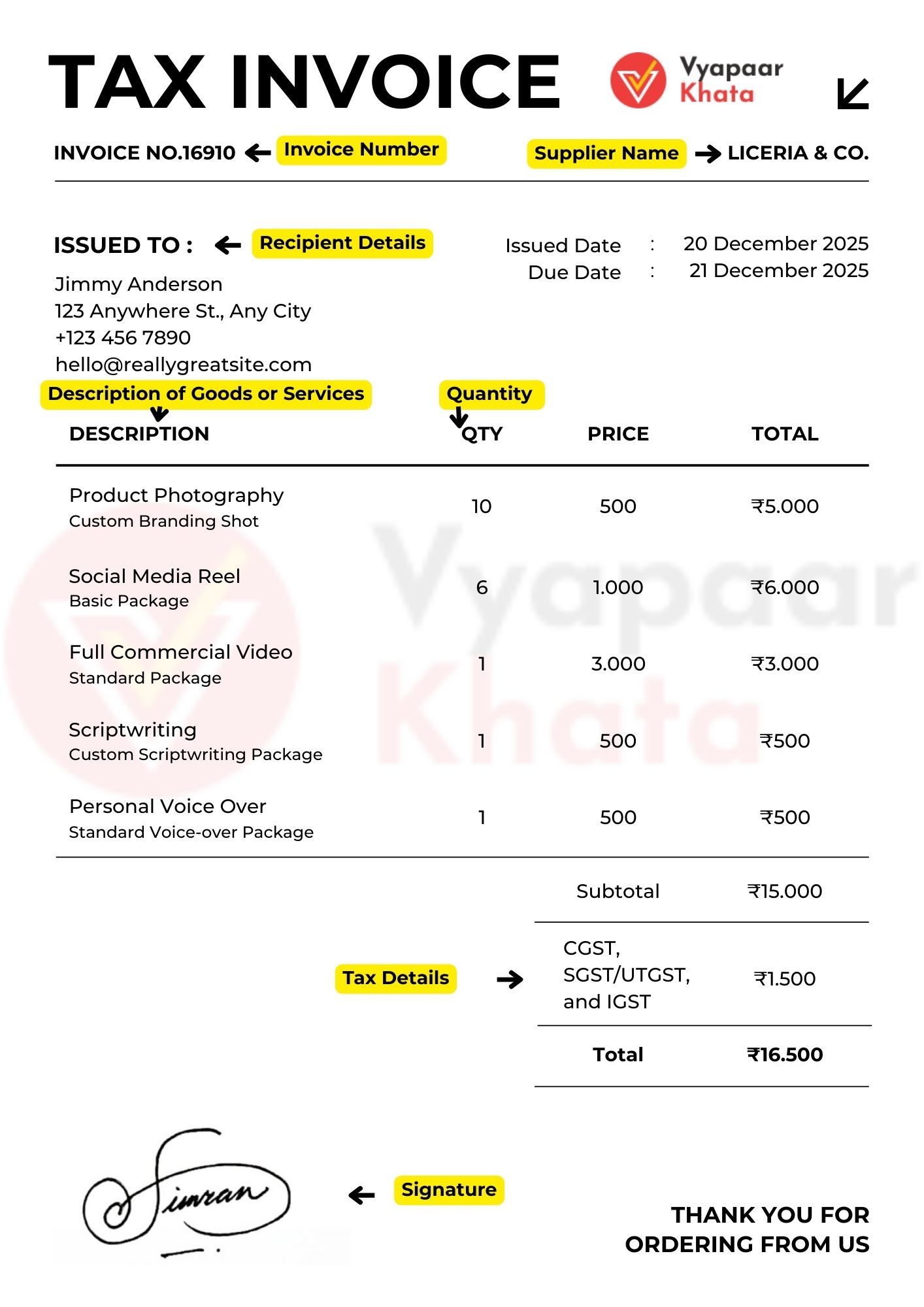
GST Invoice Format: Mandatory Components
As per Rule 46 of the CGST Rules, a GST-compliant invoice must include:
- Supplier Details: Name, address, and GSTIN.
- Invoice Number and Date: A unique serial number (up to 16 characters) and the date of issue.
- Recipient Details: Name, address, and GSTIN or UIN (if registered).
- Description of Goods or Services: Detailed description, including HSN (Harmonized System of Nomenclature) code for goods or SAC (Services Accounting Code) for services.
- Quantity and Unit: Applicable in the case of goods.
- Total Value: Taxable value after discounts or abatements.
- Tax Details: Breakdown of CGST, SGST/UTGST, and IGST, including rates and amounts.
- Place of Supply: Particularly important for inter-state transactions.
- Reverse Charge Indication: If applicable, a statement indicating that tax is payable on a reverse charge basis.
- Signature: Signature or digital signature of the supplier or authorized representative.
Note: For inter-state supplies, the place of supply along with the name of the state and its code must be mentioned.
When Can You Issue GST Invoices
If You Are a Registered GST Dealer
- You must issue a GST invoice when you supply taxable goods or services.
For Goods
- Before or at the time of removal of goods for supply to the recipient.
For Services
- Within 30 days from the date of supply of the service.
- For banks and financial institutions, the time limit is 45 days.
On Advance Payments
- You must issue a receipt voucher or advance invoice at the time of receiving advance payment for a supply.
If Supplying Exempted Goods/Services or Under the Composition Scheme
- You cannot issue a tax invoice. Instead, issue a Bill of Supply.
Exports
- GST invoice must mention “Supply meant for export on payment of IGST” or “Supply meant for export under bond or letter of undertaking without payment of IGST.”
Types of GST Invoices
- Tax Invoice: Issued for taxable supplies of goods or services.
- Bill of Supply: Issued when supplying exempted goods/services or by composition scheme taxpayers.
- Receipt Voucher: Issued when advance payment is received.
- Refund Voucher: Issued when a refund is made against an advance payment.
- Debit Note: Issued when the taxable value or tax charged in the original invoice is less than the actual amount.
- Credit Note: Issued when the taxable value or tax charged in the original invoice exceeds the actual amount.
How GST Invoice is Different From Tax Invoice:
Time Limits for Issuing Invoices
-
Goods:
Before or at the time of removal of goods for supply to the recipient.
-
Services:
Within 30 days from the date of supply of service.
For insurers, banks, NBFCs, and telecom operators, within 45 days.
Importance of GST-Compliant Invoices
- Legal Compliance: Ensures adherence to GST laws, avoiding penalties.
- Input Tax Credit (ITC): Facilitates the claim of ITC by the recipient.
- Transparency and Record-Keeping: Provides clear records for both the supplier and the recipient.
- Audit and Assessment: Simplifies the process during audits and assessments by tax authorities.
Common GST Invoice Errors, Penalties & How to Avoid Them
1. Incorrect or Missing GSTIN
- Issue: Providing an incorrect or missing GSTIN (Goods and Services Tax Identification Number) for either the supplier or the recipient.
- Consequences: Can lead to mismatches in returns, denial of Input Tax Credit (ITC), and potential penalties.
- Penalty: Up to Rs 25,000 under Section 122 of the CGST Act.
- How to Avoid: Always verify GSTINs using the official GST portal before issuing invoices.
2. Wrong HSN/SAC Codes
- Issue: Using incorrect Harmonized System of Nomenclature (HSN) or Service Accounting Codes (SAC) for goods or services.
- Consequences: Misclassification can result in incorrect tax rates being applied.
- Penalty: Up to Rs 25,000 under Section 122 of the CGST Act.
- How to Avoid: Refer to the latest HSN/SAC code list provided by the GST authorities and ensure accurate classification.
3. Calculation Errors
- Issue: Mistakes in computing taxable value, GST rates, or total invoice amounts.
- Consequences: Can lead to short payment or overpayment of taxes, affecting cash flow and compliance.
- Penalty: Interest at 18% per annum on the shortfall amount.
- How to Avoid: Use reliable accounting software with built-in GST calculators and double-check calculations before finalizing invoices.
4. Omission of Mandatory Fields
- Issue: Leaving out essential details like invoice number, date, supplier/recipient information, or tax breakdown.
- Consequences: Invoices may be considered invalid, leading to ITC denial and compliance issues.
- Penalty: Up to Rs 25,000 under Section 122 of the CGST Act.
- How to Avoid: Ensure all mandatory fields are filled in as per GST invoicing rules.
5. Non-Issuance or Delayed Issuance of Invoices
- Issue: Failing to issue invoices within the prescribed time frame.
- Consequences: Can result in non-compliance and potential penalties.
- Penalty: Rs 10,000 or the tax amount involved, whichever is higher.
- How to Avoid: Issue invoices promptly as per GST timelines: before or at the time of supply for goods, and within 30 days for services.
6. Incorrect Tax Rates Applied
- Issue: Charging the wrong GST rate on goods or services.
- Consequences: Leads to underpayment or overpayment of taxes, affecting both the supplier and recipient.
- Penalty: Interest at 18% per annum on the shortfall amount.
- How to Avoid: Stay updated with the latest GST rate notifications and apply correct rates based on HSN/SAC codes.
7. Non-Compliance with E-Invoicing Requirements
- Issue: Failing to generate e-invoices when mandated.
- Consequences: Invoices may be considered invalid, leading to ITC denial and penalties.
- Penalty: Rs 10,000 or the tax amount involved, whichever is higher.
- How to Avoid: Ensure compliance with e-invoicing requirements based on your turnover and generate e-invoices through the designated portal.
Best Practices to Prevent GST Invoice Errors
- Regular Training: Keep your accounting and billing staff updated on GST rules and changes.
- Use GST-Compliant Software: Implement reliable accounting software that adheres to GST norms and reduces manual errors.
- Periodic Audits: Conduct regular internal audits to identify and rectify discrepancies in invoicing.
- Stay Informed: Subscribe to official GST newsletters and updates to stay abreast of any changes in laws or procedures
E-Invoicing under GST
- Applicability: Mandatory for businesses with turnover exceeding specified thresholds (e.g., Rs 5 crore).
- Process:
- Invoice details are uploaded to the Invoice Registration Portal (IRP) to obtain an Invoice Reference Number (IRN).
- Benefits:
- Reduces tax evasion, ensures real-time tracking, and simplifies compliance.
- Issuing GST-compliant invoices is essential for legal compliance, smooth business operations, and facilitating ITC claims.
- Best Practices:
- Regularly update invoice formats as per the latest GST rules.
- Use reliable accounting software to minimize errors.
- Train staff on GST invoicing requirements.
By adhering to the prescribed GST invoice format and understanding its components and significance, businesses can ensure compliance, foster trust with clients, and streamline their tax processes.
