
Bookkeeping is the systematic recording of all financial transactions in your business. For small business owners, proper bookkeeping is not just a regulatory necessity—it’s a powerful tool to understand your company’s financial health and make informed decisions.
Without accurate bookkeeping, many business owners face challenges like missed tax deadlines, cash flow problems, and difficulty understanding whether the business is profitable. It can also make securing loans or attracting investors almost impossible.
This guide aims to simplify bookkeeping concepts and provide practical steps to help business owners manage their finances confidently, even without an accounting background.
What is Bookkeeping?
In simple terms, bookkeeping is keeping track of all the money that comes in and goes out of your business. It ensures that you have a clear record of income, expenses, assets, and liabilities at any given time.
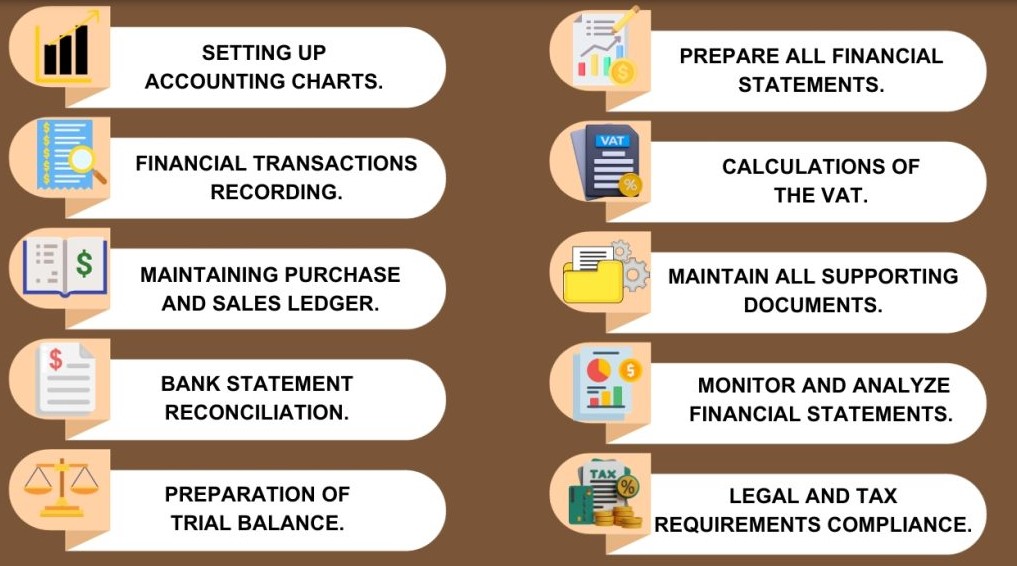
While bookkeeping focuses on recording financial transactions, accounting takes it a step further by interpreting, analyzing, and reporting this financial data to help with strategic business decisions. Think of bookkeeping as maintaining the raw data, and accounting as turning that data into actionable insights.
Bookkeeping plays a crucial role in financial management. It helps business owners:
- Monitor cash flow effectively.
- Identify profitable and loss-making areas.
- Prepare accurate financial statements.
- Stay compliant with tax and legal requirements.
Key Bookkeeping Concepts Every Business Owner Should Know
Assets, Liabilities, and Equity
These three components form the basic accounting equation:
Assets = Liabilities + Equity
- Assets: Resources owned by the business (cash, equipment, inventory).
- Liabilities: Debts or obligations (loans, unpaid bills).
- Equity: Owner’s share in the business (capital invested + retained profits).
Understanding this equation ensures that your books remain balanced and gives insight into the financial position of your business.
Revenue and Expenses
- Revenue (Income): Money earned from selling products or services.
- Expenses: Money spent to operate the business (rent, salaries, utilities).
Tracking revenue and expenses helps determine whether your business is making a profit and guides budgeting decisions.
Debits and Credits
In bookkeeping, every transaction affects at least two accounts—a system called double-entry bookkeeping:
- Debit (Dr): Records money coming into an account or an increase in assets.
- Credit (Cr): Records money leaving an account or an increase in liabilities/equity.
For beginners, the key is to understand that debits and credits always balance each other, keeping your books accurate.
Cash vs. Accrual Accounting
- Cash Accounting: Records transactions only when money changes hands. Simple and suitable for very small businesses.
- Accrual Accounting: Records income and expenses when they are earned or incurred, regardless of cash movement. Provides a more accurate picture of financial health.
Choosing the right method depends on your business size, complexity, and reporting needs.
Common Bookkeeping Methods
Single-Entry Bookkeeping
This is a straightforward method where each transaction is recorded once, usually in a spreadsheet or ledger. It’s easy to maintain but may not provide a complete picture of your financial position. Ideal for very small businesses with simple transactions.
Double-Entry Bookkeeping
In double-entry bookkeeping, each transaction affects two accounts (debit and credit), ensuring that the accounting equation always balances. This method provides greater accuracy, reduces errors, and makes it easier to generate financial statements. Most businesses adopt this method as they grow.
Choosing the Right Method for Your Business
- Single-entry pros: Simple, low-cost, easy for beginners.
- Single-entry cons: Limited reporting, prone to errors.
- Double-entry pros: Accurate, supports detailed reporting, essential for scaling.
- Double-entry cons: Slightly more complex and time-consuming.
For most growing businesses, double-entry bookkeeping is recommended because it provides a more complete and reliable financial picture.
Essential Bookkeeping Tools
Having the right tools makes bookkeeping easier, more accurate, and less time-consuming. Depending on the size and complexity of your business, you can choose between manual methods or digital tools:
Manual Bookkeeping
- Ledgers and Journals: Traditionally, businesses used physical ledgers to record transactions. Each sale, expense, or payment is written down chronologically.
- Spreadsheets: Programs like Microsoft Excel or Google Sheets are a modern manual alternative. You can create templates to track income, expenses, and even generate basic reports.
Pros: Low cost, easy to start.
Cons: Time-consuming, error-prone, not ideal for scaling.
Accounting Software Options
Digital tools automate much of the bookkeeping process, reduce errors, and make reporting simple. Some popular options include:
- Vyapaarkhata: Ideal for SME's offers invoicing, and stock managment in one solution.
- QuickBooks: Ideal for small to medium-sized businesses; offers invoicing, payroll, and reporting.
- Zoho Books: Cloud-based, integrates with CRM tools, and supports GST compliance in India.
- Xero: Cloud software with bank reconciliation, reporting, and multi-currency support.
Tips for Choosing Tools:
- Start with basic features if your business is small.
- Look for automation options to reduce repetitive tasks.
- Ensure integration capabilities with your bank and other business apps.
- Choose software with scalable features as your business grows.
Step-by-Step Guide to Basic Bookkeeping
Follow these steps to maintain organized and accurate financial records:
- Open a Separate Business Bank Account
Keeping personal and business finances separate avoids confusion and simplifies tax filing. - Keep Track of All Income and Expenses
Record every transaction, whether it’s a sale, purchase, or payment. This ensures no money is unaccounted for. - Record Transactions Regularly
Don’t wait until month-end. Daily or weekly updates prevent mistakes and save time. - Reconcile Bank Statements Monthly
Compare your records with your bank statements to catch discrepancies early. - Categorize Expenses Correctly
Organize expenses into categories like utilities, salaries, rent, and supplies. This helps in budgeting and reporting. - Prepare Basic Financial Statements
- Profit & Loss Statement: Shows revenue, expenses, and net profit.
- Balance Sheet: Provides a snapshot of assets, liabilities, and equity.
Consistently following these steps creates a clear financial picture and builds a foundation for growth.
Tips for Maintaining Accurate Records
Accuracy is key in bookkeeping. Here are best practices:
- Keep Receipts and Invoices Organized: Store them digitally or physically. This ensures evidence of all transactions is available for audits.
- Set a Regular Bookkeeping Schedule: Dedicate time weekly or bi-weekly to update records. Consistency avoids backlog and errors.
- Review Financial Statements Regularly: Check your profit/loss and balance sheet to spot mistakes or unusual trends.
- Seek Professional Help When Needed: Accountants or bookkeepers can guide you, especially for tax filing or complex transactions.
Common Bookkeeping Mistakes to Avoid
Even small errors can snowball into big problems. Avoid these pitfalls:
- Mixing Personal and Business Finances: Makes tracking expenses and tax filing difficult.
- Delaying Recording of Transactions: Leads to incomplete records and increased errors.
- Ignoring Small Expenses: Minor costs add up and affect profitability analysis.
- Not Reconciling Accounts Regularly: Unreconciled accounts can hide discrepancies and fraud.
Being vigilant and disciplined can prevent these common mistakes.
Benefits of Good Bookkeeping
Accurate bookkeeping offers numerous advantages:
- Better Financial Visibility and Decision-Making: Understand profits, cash flow, and financial position.
- Easier Tax Filing and Compliance: Organized records simplify GST, income tax, and other statutory filings.
- Helps Secure Loans or Attract Investors: Clean financial statements build credibility with lenders and investors.
- Prevents Financial Mismanagement and Fraud: Regular tracking and reconciliation reduce errors and unauthorized transactions.
Good bookkeeping is not just about compliance; it’s about creating a roadmap for business growth.
Bookkeeping may seem tedious at first, but it is an essential skill for any business owner. Maintaining accurate records ensures financial clarity, simplifies tax filing, and supports strategic decisions.
Start small: choose a bookkeeping method, set up a routine, and gradually implement tools that fit your business. Consistency is key—over time, disciplined bookkeeping becomes an invaluable asset, helping your business thrive and scale efficiently.
