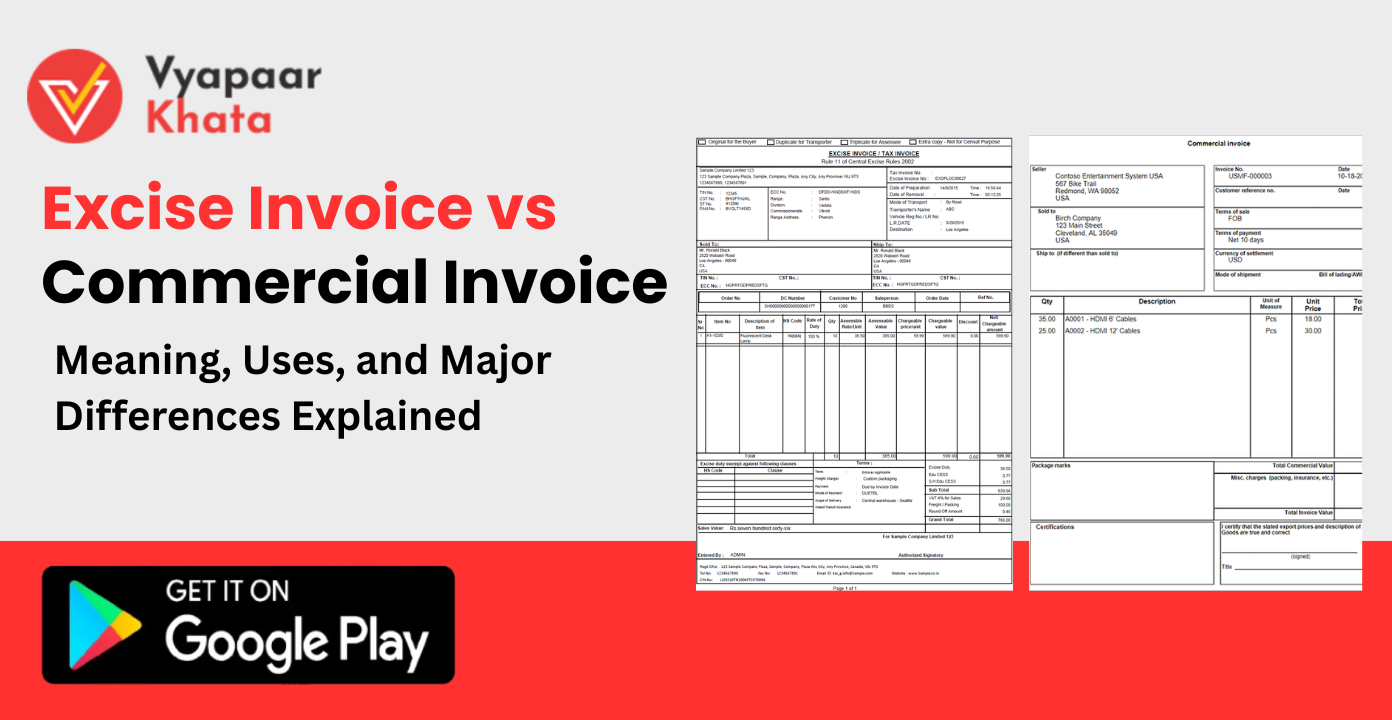
Invoices are one of the most essential documents in business, serving as proof of sale, a basis for accounting, and a key instrument for taxation and trade compliance. Whether you are a manufacturer, wholesaler, or retailer, accurate invoicing ensures smooth financial management and legal adherence.
However, many businesses often get confused between excise invoices and commercial invoices, especially in the context of Indian taxation. Both serve as invoices but have distinct purposes and regulatory requirements.
This article aims to clarify the meaning, uses, and major differences between excise invoices and commercial invoices, helping businesses comply with legal norms and avoid errors in documentation.
What Is a Commercial Invoice?
An invoice is a document issued by a seller to a buyer, detailing the goods or services provided and the amount payable. It acts as a formal request for payment and serves as proof of a transaction.
Role of invoices in business:
- Accounting: Helps in maintaining accurate records of sales and purchases.
- Taxation: Forms the basis for tax calculation and filing.
- Compliance: Required for audits, legal verification, and trade documentation.
Common types of invoices in India:
- Commercial Invoice – used in domestic and international trade.
- Excise Invoice – specific to excisable goods under pre-GST regulations.
- Retail Invoice – for end customers in retail sales.
- Proforma Invoice – issued before the actual sale, usually for quotations.
What Is an Excise Invoice?
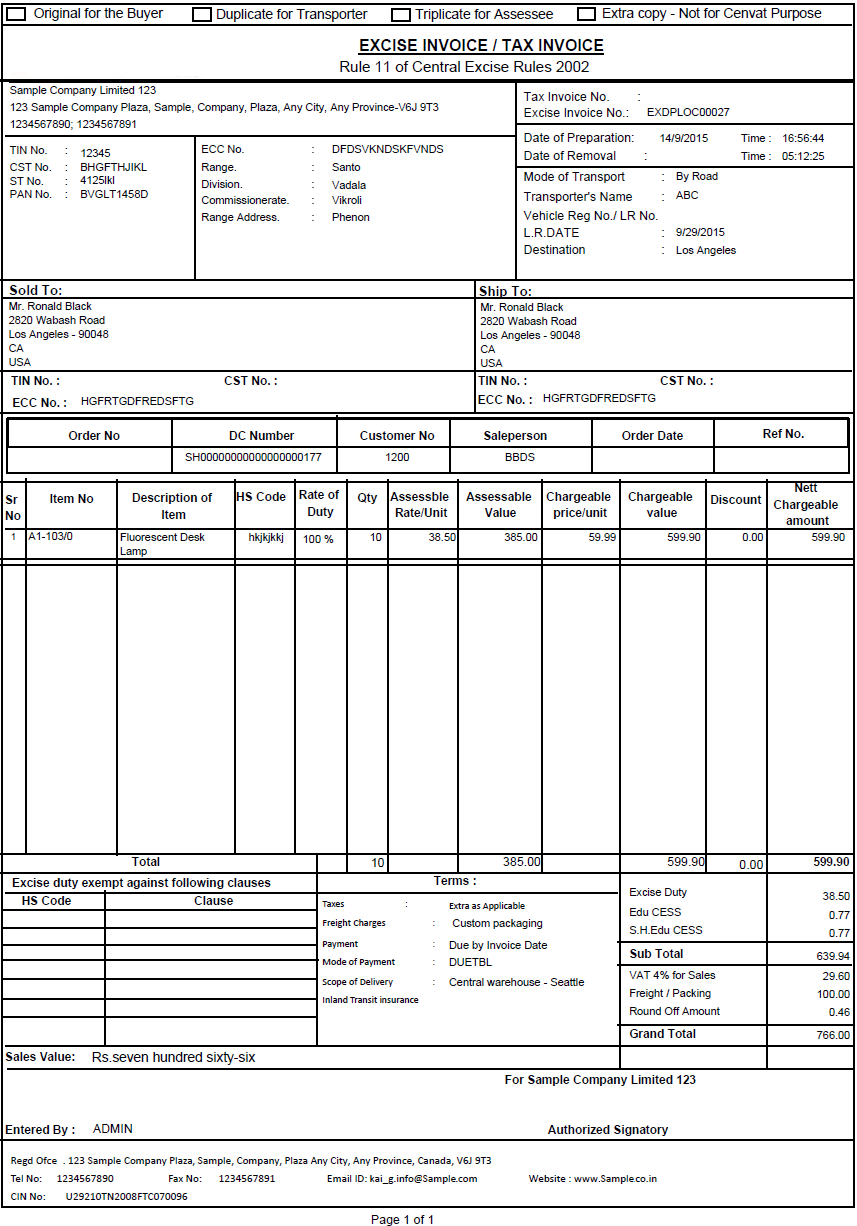
An excise invoice is a legally mandated document issued by manufacturers registered under the Central Excise Act (pre-GST era). It serves as evidence of excise duty liability and ensures proper taxation of excisable goods.
Purpose:
- To declare excise duty payable on manufactured goods.
- To ensure smooth movement of excisable goods between manufacturers, distributors, and dealers.
- To facilitate compliance and claim of CENVAT credit (pre-GST).
Key Features of an Excise Invoice
- Issued only by excise-registered manufacturers.
- Contains details of excise duty applicable on goods.
- Maintains serial numbering and follows a statutory format prescribed by the government.
- Acts as a legal document for the movement of excisable goods.
Information Included in an Excise Invoice
An excise invoice typically contains the following details:
- Manufacturer Details: Name, address, and excise registration number.
- Goods Description: Name, classification, and HSN/SAC code.
- Quantity and Value: Number of units and assessable value of goods.
- Excise Duty Details: Duty rate, duty amount, and total duty payable.
- Invoice Details: Date, serial number, and other statutory references.
Uses of Excise Invoice
- Proof of excise duty payment to government authorities.
- CENVAT Credit Claims: Helps buyers or distributors claim input credit for excise duty (pre-GST).
- Legal Compliance: Mandatory for transporting excisable goods and ensuring accountability.
What Is a Commercial Invoice?
A commercial invoice is a document issued by a seller to a buyer that lists the goods or services provided, along with the amount payable. It serves as a primary record of a sale transaction.
Role in trade:
- Domestic trade: Acts as proof of sale and demand for payment between businesses.
- International trade: Used for customs clearance, shipment documentation, and determining duties and taxes.
Key Features of a Commercial Invoice
- Issued by the seller to the buyer.
- Serves as the primary document for any sales transaction.
- Acts as a formal demand for payment and supports accounting and legal compliance.
- Can be used for both domestic and international trade.
Information Included in a Commercial Invoice
A commercial invoice generally contains:
- Seller and buyer details: Name, address, and contact information.
- Invoice details: Number, date, and reference to purchase order.
- Goods or services description: Name, specifications, and classification.
- Quantity and price: Unit price, total value, and applicable taxes.
- Additional details: Discounts, shipping costs, payment terms, and currency (for international trade).
Uses of Commercial Invoice
- Accounting and bookkeeping: Records sales revenue and supports tax filings.
- Customs clearance: Required for import/export of goods.
- Proof of sale and ownership transfer: Demonstrates legal ownership of goods.
Excise Invoice vs Commercial Invoice: Key Differences
| Feature | Excise Invoice | Commercial Invoice |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | Invoice for excise duty on manufactured goods | Invoice for sale of goods/services |
| Issuing Authority | Manufacturer registered under excise laws | Seller of goods/services |
| Purpose | Compliance with excise duty regulations | Record of sale, payment demand |
| Legal Applicability | Pre-GST law for excisable goods | Domestic & international trade law |
| Tax Components | Excise duty details | GST, VAT, or other applicable taxes |
| Usage | Mostly domestic movement of excisable goods | Domestic & international trade transactions |
Difference Explained in Simple Terms
- Excise Invoice: Tax-focused, compliance-driven, mandatory for excisable goods.
- Commercial Invoice: Transaction-focused, used for business records, payments, and trade documentation.
- Excise invoices ensure legal compliance, whereas commercial invoices support business operations and accounting.
Applicability After GST in India
- Post-GST scenario: Traditional excise invoices are mostly replaced by GST tax invoices.
- Goods still under excise: Petroleum products, alcohol, and tobacco still require excise documentation.
- GST has simplified invoicing for most businesses, merging tax and commercial details into a single invoice.
Excise Invoice and Commercial Invoice in Business Operations
From Manufacturer’s Perspective
- Excise invoice: Required for excisable goods to show duty payment.
- Commercial invoice: Needed for sales transactions and business records.
- Both invoices may coexist, especially when excisable goods are sold to distributors or dealers.
From Trader and Exporter’s Perspective
- Commercial invoice: Critical for customs clearance, shipping, and accounting.
- Excise invoice: Less relevant post-GST, except for restricted goods.
- Accurate invoicing ensures smooth logistics, legal compliance, and proper tax filing.
Common Mistakes and Misconceptions
- Confusing excise invoice with a tax invoice.
- Incorrect calculation of duty, GST, or taxes.
- Missing mandatory details like serial number, invoice date, or registration numbers.
- Using a commercial invoice in place of an excise invoice for excisable goods.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. Is excise invoice still applicable in India?
A: Mostly replaced by GST invoices; still applicable for petroleum, alcohol, and tobacco.
Q2. Can one document serve as both excise and commercial invoice?
A: In some cases pre-GST, yes; post-GST, the tax invoice often serves both purposes except for restricted excisable goods.
Q3. Is a commercial invoice mandatory for exports?
A: Yes, it is required for customs clearance, export documentation, and payment claims.
Q4. Who is authorized to issue an excise invoice?
A: Only manufacturers registered under excise law can issue excise invoices.
- Excise invoices are primarily tax and compliance-focused, while commercial invoices record sales and support trade operations.
- Importance: Choosing the correct invoice type ensures legal compliance, smooth trade, and proper accounting.
- Final takeaway: Businesses should maintain clarity between the two and use software solutions like
Vyaaparkhata Invoice Creation Software to generate excise, commercial, and GST-compliant invoices easily and free of cost.
