
Invoicing is a crucial part of every business transaction. An invoice acts as a written record of goods sold or services provided between a seller and a buyer. It includes important details such as product descriptions, quantities, prices, taxes, payment terms, and seller–buyer information. Invoices help businesses track sales, manage payments, and maintain proper financial records.
Importance of Understanding Different Invoice Types
Different business situations require different types of invoices. Common invoice types include proforma invoices, tax invoices, commercial invoices, and credit notes. Understanding the purpose and usage of each invoice type helps businesses comply with legal requirements, avoid accounting errors, and ensure smooth transactions. Using the wrong invoice at the wrong stage can lead to payment delays or tax issues.
Why Confusion Often Arises Between Proforma and Tax Invoices
Confusion between proforma invoices and tax invoices occurs because both documents look similar and contain many common details. However, their purpose, legal validity, and accounting impact are very different. Many businesses mistakenly treat a proforma invoice as a final bill, which can create misunderstandings related to payments, taxation, and compliance.
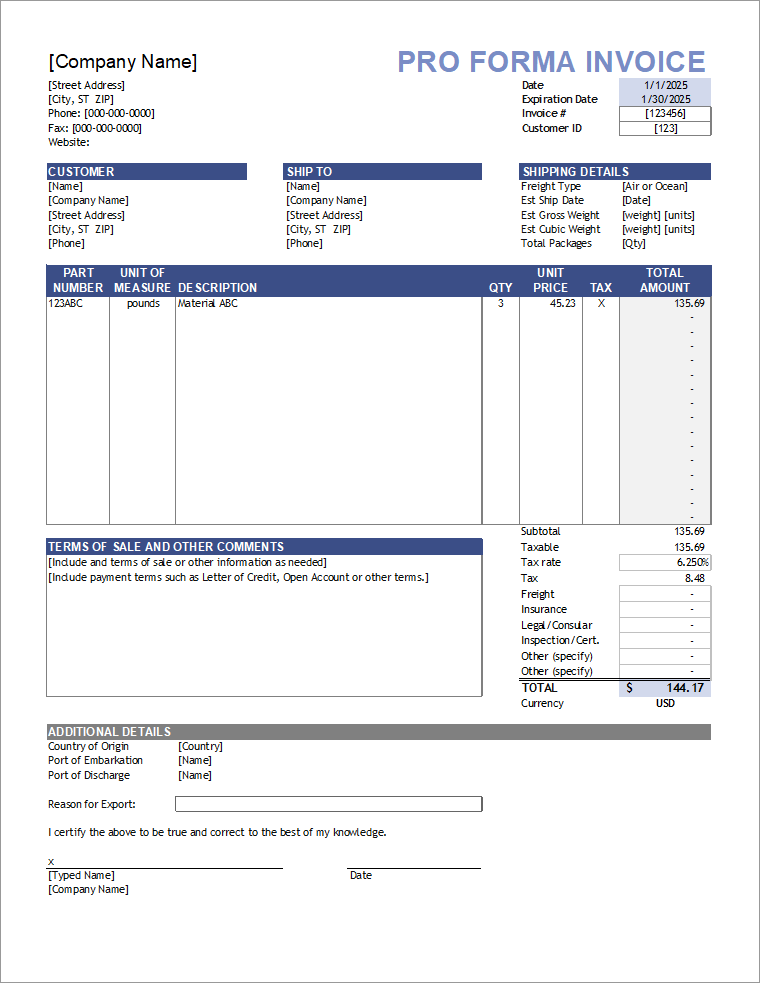
What Is a Proforma Invoice?
A proforma invoice is a preliminary document issued by a seller to a buyer before the actual sale takes place. It provides an estimated cost of goods or services, including prices, quantities, and other terms. A proforma invoice is not a demand for payment and does not confirm a completed sale.
Purpose and Role in Business Transactions
The main purpose of a proforma invoice is to give the buyer a clear idea of the expected cost and terms of a transaction. It helps buyers evaluate pricing, arrange funds, seek internal approvals, or apply for import licenses. For sellers, it acts as a formal quotation and helps avoid disputes later.
When a Proforma Invoice Is Issued
A proforma invoice is usually issued:
- Before confirming an order
- During price negotiation
- Before receiving advance payment
- Prior to international shipments
- When a buyer requests a quotation in invoice format
It is commonly used in both domestic and international trade.
Legal Validity and Accounting Impact
A proforma invoice has no legal or tax validity. It cannot be used for tax filing, GST input credit, or revenue recognition. Since no actual sale has occurred, it is not recorded in the seller’s accounting books as income. It is only a reference document and not a legally enforceable invoice.
Key Features of a Proforma Invoice
Non-Binding Nature
A proforma invoice is non-binding, meaning it does not legally obligate the buyer to make payment or the seller to deliver goods. The final transaction terms can still change before issuing the tax invoice or commercial invoice.
Contents Typically Included
A proforma invoice usually includes:
- Seller and buyer details
- Description of goods or services
- Quantity and unit price
- Total estimated value
- Delivery terms
- Payment terms
- Validity period of the offer
- Proforma invoice number and date
It clearly mentions “Proforma Invoice” to avoid confusion with a tax invoice.
Use in Quotations and Advance Payments
Many businesses use proforma invoices as formal quotations. Buyers often rely on them to make advance payments or secure purchase approvals. However, even if an advance payment is made, a tax invoice must be issued separately once the sale is confirmed.
Role in Import-Export and Customs Clearance
In international trade, proforma invoices play a key role in:
- Import-export documentation
- Applying for import licenses
- Customs valuation
- Foreign exchange approvals
Customs authorities may use proforma invoices for preliminary assessment, but final clearance requires a commercial or tax invoice.
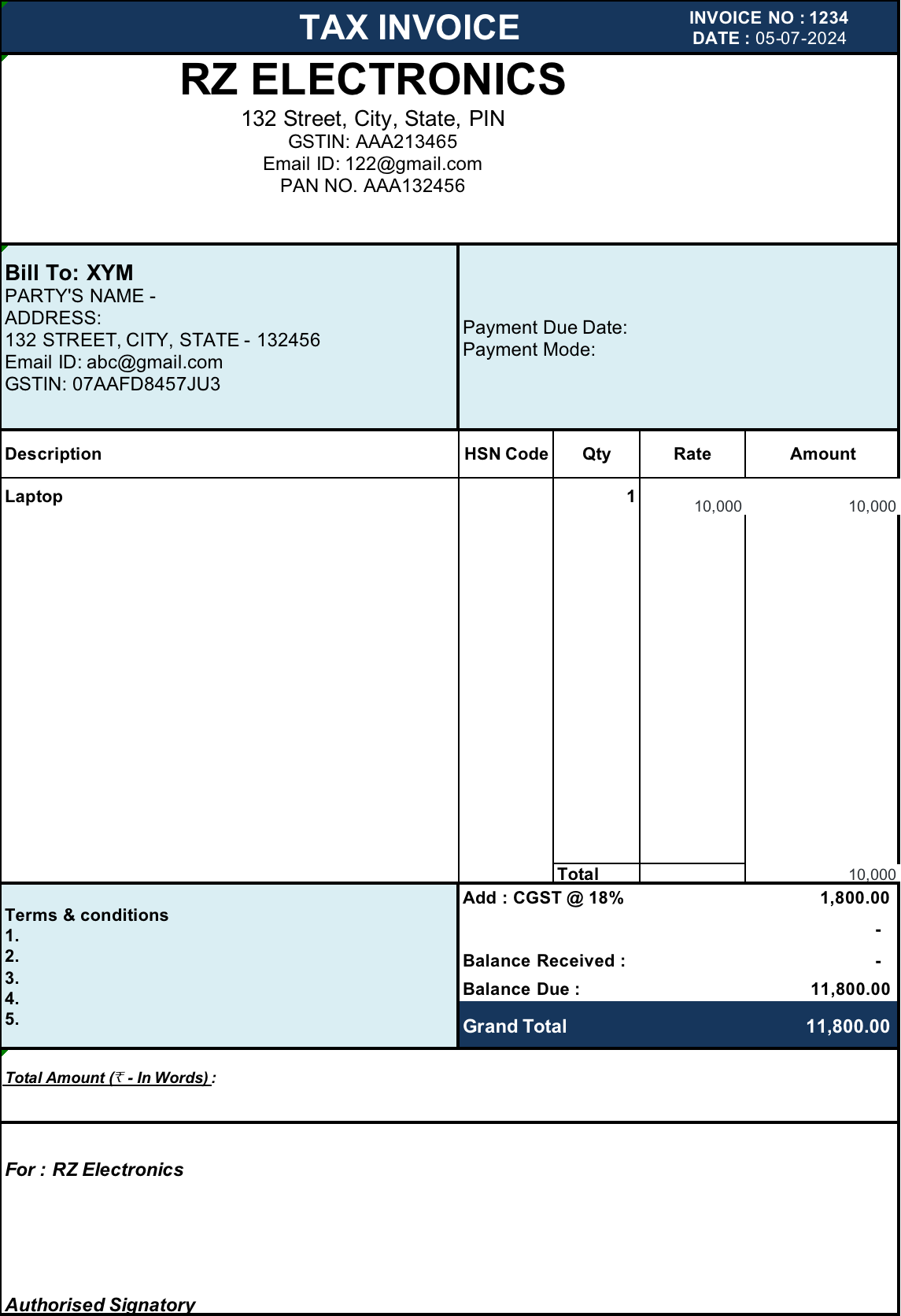
What Is a Tax Invoice?
A tax invoice is a legally valid document issued by a seller to a buyer after the sale of goods or services. It confirms that a transaction has taken place and shows the exact amount payable, including applicable taxes such as GST or VAT. A tax invoice is the final billing document used for payment, taxation, and accounting purposes.
Legal Significance Under Tax Laws (GST, VAT, etc.)
Under tax laws like GST in India or VAT in other countries, issuing a tax invoice is mandatory for registered businesses. The tax invoice serves as legal proof of sale and tax collection. Authorities rely on it to verify tax liability, audit records, and ensure compliance. Failure to issue a proper tax invoice can lead to penalties, interest, or legal action.
When a Tax Invoice Is Issued
A tax invoice is issued:
- After the supply of goods or services
- At the time of delivery or completion of service
- When ownership of goods is transferred
- As per timelines defined under tax laws
In GST, the tax invoice must be issued within a specified time limit depending on whether the supply involves goods or services.
Role in Tax Compliance and Record Keeping
Tax invoices play a crucial role in maintaining accurate financial and tax records. They help businesses:
- Report sales correctly in tax returns
- Calculate tax liability
- Maintain audit-ready documentation
- Ensure transparency in transactions
For buyers, tax invoices act as proof of purchase and tax paid.
Key Features of a Tax Invoice
Mandatory Details Required by Law
A tax invoice must contain specific details as prescribed by law, including:
- Seller’s name, address, and GST/VAT registration number
- Buyer’s name and address
- Unique invoice number and date
- Description of goods or services
- Quantity and unit price
- Taxable value
- Applicable tax rates (CGST, SGST, IGST, or VAT)
- Total invoice value
- Place of supply and HSN/SAC codes (where applicable)
Missing mandatory details can make the invoice invalid.
Binding and Final Document
A tax invoice is a binding and final document. Once issued, it legally confirms the transaction. Both buyer and seller are obligated to follow the terms mentioned, including payment and tax settlement.
Importance for Claiming Input Tax Credit (ITC)
For GST-registered buyers, a valid tax invoice is essential to claim Input Tax Credit (ITC). Without a proper tax invoice:
- ITC cannot be claimed
- Tax paid becomes a cost
- Compliance issues may arise during audits
This makes tax invoices extremely important for business profitability.
Impact on Accounting and Taxation
Tax invoices directly impact:
- Sales revenue recognition
- Tax payable calculations
- Monthly and annual tax returns
- Financial statements
They are recorded in accounting books and used to reconcile sales, taxes, and payments.
Proforma Invoice vs Tax Invoice: Detailed Comparison
Understanding the difference between a proforma invoice and a tax invoice helps businesses use the right document at the right stage and avoid legal or accounting mistakes.
Key Differences Explained
- Purpose: A proforma invoice is an estimate or quotation, while a tax invoice confirms an actual sale.
- Legal Validity: Proforma invoices have no legal standing, but tax invoices are legally enforceable.
- Timing: Proforma invoices are issued before the sale; tax invoices are issued after the sale.
- Tax Applicability: No tax liability arises from a proforma invoice, but taxes are applicable on a tax invoice.
- Accounting Treatment: Proforma invoices are not recorded in books, whereas tax invoices are recorded as income.
Proforma Invoice vs Tax Invoice
| Basis | Proforma Invoice | Tax Invoice |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Price estimation or quotation | Final billing for completed sale |
| Legal Validity | Not legally valid | Legally valid document |
| Timing of Issuance | Before sale or order confirmation | After sale or supply |
| Tax Applicability | No tax liability | Tax is charged and payable |
| Accounting Treatment | Not recorded in accounts | Recorded as sales revenue |
| Input Tax Credit (ITC) | Not eligible | Eligible (subject to conditions) |
| Payment Obligation | Not mandatory | Mandatory for buyer |
| Use in Compliance | Informational only | Essential for tax filing and audits |
When Should You Use a Proforma Invoice?
A proforma invoice should be used before the actual sale takes place. It helps both the buyer and seller align on pricing, terms, and expectations without creating legal or tax obligations.
During Price Negotiations
Proforma invoices are commonly used during price discussions. They provide a clear breakdown of costs, quantities, and terms, allowing buyers to negotiate prices or request changes before confirming the order. This reduces misunderstandings later.
For Advance Payment Requests
Many businesses request advance payments based on a proforma invoice. Since it shows estimated costs and payment terms, buyers can arrange funds confidently. However, the seller must issue a tax invoice separately once the sale is completed.
In International Trade Scenarios
In import–export transactions, proforma invoices are widely used for:
- Import license applications
- Customs valuation (preliminary)
- Foreign exchange approvals
- Buyer confirmation before shipment
They help international buyers understand pricing and shipment terms before committing.
For Customer Approval Before Final Billing
Large organizations often require internal approvals before placing orders. A proforma invoice serves as an official quotation that buyers can submit for approval before the final tax invoice is issued.
When Should You Issue a Tax Invoice?
A tax invoice should be issued only after the actual supply of goods or services. It is mandatory for legal, accounting, and tax compliance.
After Supply of Goods or Services
A tax invoice is issued once:
- Goods are delivered
- Services are completed
- Ownership of goods is transferred
This confirms that a taxable supply has taken place.
As Per Statutory Timelines
Under GST and other tax laws, tax invoices must be issued within specified timelines. Delayed issuance can attract penalties and compliance issues.
For GST/VAT Compliance
Tax invoices are essential for:
- Charging and collecting tax
- Filing GST/VAT returns
- Reporting outward supplies
Without a valid tax invoice, tax compliance is incomplete.
For Final Payment and Tax Reporting
Tax invoices act as the final payment request. They are used for:
- Buyer payments
- Seller tax liability calculation
- Monthly, quarterly, and annual tax reporting
Common Mistakes Businesses Make
Many businesses face compliance and accounting problems due to incorrect invoice usage. Some common mistakes include:
Treating Proforma Invoices as Tax Invoices
One of the most common errors is treating a proforma invoice as a final bill. Since proforma invoices have no legal or tax validity, this can lead to incorrect tax reporting and payment disputes.
Incorrect Tax Calculations
Errors in tax rates, HSN/SAC codes, or taxable value can make tax invoices invalid. Incorrect calculations may result in excess tax payment or penalties.
Delayed Issuance of Tax Invoices
Issuing tax invoices late violates statutory timelines, especially under GST. This can lead to interest, penalties, and compliance notices from tax authorities.
Documentation Errors Affecting Compliance
Missing mandatory details such as GST number, invoice date, or place of supply can prevent buyers from claiming Input Tax Credit and create audit issues.
Proforma Invoice and Tax Invoice Under GST (India-Specific)
GST Provisions Related to Proforma Invoices
Under GST law, proforma invoices are not recognized as tax documents. They are purely informational and do not create tax liability. No GST is payable or collectible based on a proforma invoice.
Mandatory Requirements for Tax Invoices Under GST
A valid GST tax invoice must include:
- Supplier’s name, address, and GSTIN
- Invoice number and date
- Buyer’s details (for registered buyers)
- Description of goods or services
- HSN/SAC codes
- Taxable value
- GST rates and amounts (CGST, SGST, IGST)
- Place of supply
- Total invoice value
Only invoices meeting these conditions are accepted for compliance and ITC claims.
Consequences of Non-Compliance
Failure to issue proper tax invoices under GST can result in:
- Monetary penalties
- Interest on unpaid tax
- Disallowance of Input Tax Credit
- Increased scrutiny during audits
Consistent non-compliance may lead to legal action.
Benefits of Using the Correct Invoice Type
Using the right invoice at the right stage brings multiple operational and compliance advantages.
Improved Transparency
Clear distinction between proforma and tax invoices ensures transparency in pricing, taxation, and payment expectations for both buyers and sellers.
Better Customer Communication
Proforma invoices help set expectations early, while tax invoices provide clear, legally valid billing. This reduces disputes and builds customer trust.
Smooth Accounting and Audits
Correct invoicing ensures accurate record keeping, easy reconciliation, and hassle-free audits. It also simplifies GST return filing.
Reduced Risk of Tax Penalties
Proper use of tax invoices helps businesses comply with statutory requirements, reducing the risk of penalties, interest, and legal issues.
FAQs on Proforma Invoice vs Tax Invoice
Is a proforma invoice legally valid?
No, a proforma invoice is not legally valid. It is only an informational or preliminary document issued before the actual sale. It does not create any legal obligation for payment and cannot be used as proof of sale or for tax filing.
Can GST be charged on a proforma invoice?
No, GST cannot be charged or collected on a proforma invoice. Since it does not confirm a taxable supply, GST liability does not arise. GST can only be charged when a valid tax invoice is issued after the supply of goods or services.
Can a proforma invoice be converted into a tax invoice?
A proforma invoice itself cannot be “converted” into a tax invoice. However, once the sale is confirmed, the seller can issue a separate tax invoice based on the details mentioned in the proforma invoice. The tax invoice must have a unique invoice number and meet all legal requirements.
Is payment mandatory against a proforma invoice?
No, payment is not mandatory against a proforma invoice. However, buyers may choose to make an advance payment based on it. Even in such cases, the seller must issue a proper tax invoice after the supply to remain compliant with tax laws.
Summary of Key Differences
A proforma invoice is a pre-sale document used for estimation, negotiation, and approval, while a tax invoice is a post-sale legal document used for billing, taxation, and compliance. The proforma invoice has no legal or tax validity, whereas the tax invoice is mandatory under GST and other tax laws.
Importance of Choosing the Right Invoice
Using the correct invoice at the right stage helps businesses avoid payment disputes, accounting errors, and compliance issues. It also ensures clarity between buyers and sellers and supports smooth business operations.
Final Compliance and Best Practice Tips
- Use proforma invoices only for quotations and advance discussions
- Issue tax invoices strictly within statutory timelines
- Ensure all mandatory details are included in tax invoices
- Maintain proper records for audits and GST filing
- Educate your accounting and sales teams on invoice usage
By understanding the difference between proforma invoices and tax invoices, businesses can improve transparency, ensure compliance, and build stronger professional relationships.
