In the world of business and taxation, proper documentation of sales and purchases is crucial. In India, under the Goods and Services Tax (GST) regime, two types of documents are commonly used to record transactions: Tax Invoice and Bill of Supply. While they might seem similar, each serves a distinct purpose and carries different legal implications. Understanding the difference is essential for businesses to ensure compliance, avoid penalties, and manage Input Tax Credit (ITC) effectively.
What is a Tax Invoice?
A Tax Invoice is a document issued by a registered GST supplier for taxable goods or services. It reflects the value of the supply along with the GST charged.
Key Facts About Tax Invoice:
- It is mandatory for taxable supplies.
- It enables the recipient to claim Input Tax Credit (ITC).
- Every registered GST supplier must issue a tax invoice within a stipulated time:
- Goods: Before or at the time of delivery.
- Services: Within 30 days from the date of supply.
- A tax invoice must contain:
- Supplier’s name, address, and GSTIN
- Invoice number and date (unique and sequential)
- Recipient’s name, address, and GSTIN (if registered)
- HSN (Harmonized System of Nomenclature) or SAC (Service Accounting Code)
- Description, quantity, and value of goods/services
- GST rate applied (CGST, SGST, IGST)
- Total taxable value and total GST amount
- Grand total including GST
Example:
If a registered supplier sells electronic gadgets worth ?50,000 with 18% GST, the tax invoice will show ?9,000 as GST (?4,500 CGST + ?4,500 SGST) and total ?59,000 payable.
Legal Significance:
Issuing a tax invoice is mandatory for compliance under GST. Non-issuance or incorrect invoices can attract penalties up to ?25,000 under GST law.
What is a Bill of Supply?
A Bill of Supply is a document issued when GST is not applicable on the supply of goods or services. This generally applies to:
- Businesses under the Composition Scheme (turnover less than ?2 crore in most states)
- Exempted goods and services
- Supplies where the recipient is unregistered under GST
Key Facts About Bill of Supply:
- No GST is charged; hence, the recipient cannot claim ITC.
- It is issued in place of a tax invoice.
- Mandatory details in a bill of supply:
- Supplier’s name, address, and GSTIN (if registered)
- Bill number and date
- Recipient’s details (optional if unregistered)
- Description, quantity, and value of goods/services
- Statement: “Tax is not applicable” or “Supplied under composition scheme”
Example:
A restaurant under the composition scheme sells a meal for ?1,000. The bill of supply will mention only the amount ?1,000, without any GST, and note that tax is not applicable.
Legal Significance:
Issuing a bill of supply ensures compliance for exempt or composition supplies. Misusing it can lead to scrutiny from GST authorities.
Key Differences Between Tax Invoice and Bill of Supply
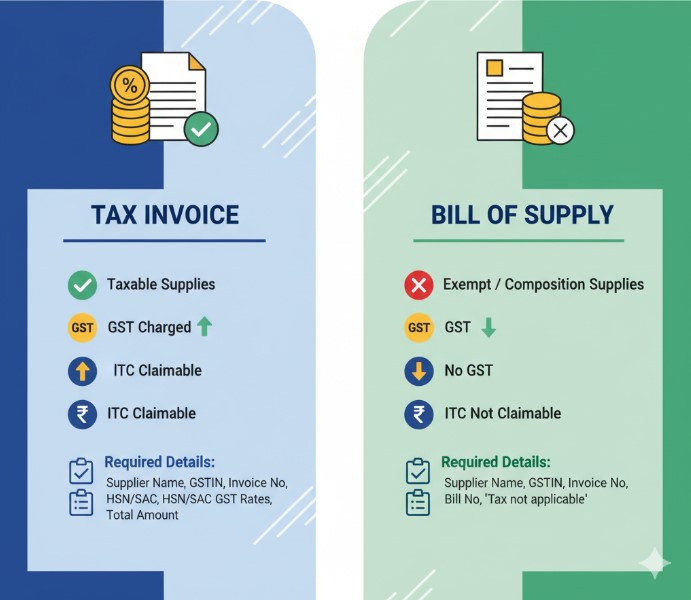
| Feature | Tax Invoice | Bill of Supply |
|---|---|---|
| Applicability | Taxable supplies of goods/services | Exempted supplies or composition scheme |
| GST Charged | Yes | No |
| Input Tax Credit (ITC) | Can be claimed by recipient | Cannot be claimed |
| Document Type | Invoice | Bill of Supply |
| Mandatory for Registered Supplier | Yes | Yes (if supply is exempt/composition) |
| Time of Issue | Goods: at or before delivery, Services: within 30 days | At the time of supply |
Format and Examples
Sample Tax Invoice Layout:
- Supplier: ABC Electronics, GSTIN: 27ABCDE1234F1Z5
- Invoice No: 101, Date: 20/09/2025
- Customer: XYZ Pvt. Ltd., GSTIN: 27XYZDE5678G1Z9
- Description: Laptop, Quantity: 2, Rate: Rs 25,000 each
- Total Value: Rs 50,000
- CGST 9%: Rs 4,500, SGST 9%: Rs 4,500
- Grand Total: Rs 59,000
Sample Bill of Supply Layout:
- Supplier: MNO Traders, GSTIN: 27MNOPQ1234L1Z6
- Bill No: 201, Date: 20/09/2025
- Customer: Local Buyer (Unregistered)
- Description: Grocery items, Quantity: 10, Rate: Rs 1,000 each
- Total Value: Rs 10,000
- Note: “Tax is not applicable as supply is exempt under GST”
Penalties and Compliance
- Issuing a wrong document (bill of supply instead of tax invoice) can lead to penalties.
- Businesses must maintain sequential numbering and proper records.
- Compliance ensures smooth GST audits and avoids input credit rejection.
FAQs
Q1. Can a composition dealer issue a tax invoice?
No, a composition dealer must issue a bill of supply for all their sales.
Q2. Can ITC be claimed from a bill of supply?
No, ITC cannot be claimed as GST is not charged.
Q3. What if GST is mistakenly charged on exempt supplies?
The supplier must rectify the invoice and issue a corrected bill of supply.
Q4. Are bills of supply required for inter-state supplies?
Yes, even for inter-state exempt supplies or composition scheme sales.
Correct documentation under GST is not just a legal requirement but also ensures smooth business operations. A Tax Invoice is used for taxable supplies and enables ITC, while a Bill of Supply is for exempted supplies or composition dealers where GST is not applicable. Understanding the difference helps businesses maintain compliance, avoid penalties, and manage finances effectively.
