The Goods and Services Tax (GST) system in India has transformed the way businesses issue invoices and determine their tax liabilities. One of the most crucial terms in GST compliance is invoice value. It directly affects tax liability, Input Tax Credit (ITC), compliance filings, and overall financial transparency in business transactions.
Many businesses confuse invoice value with taxable value, which can lead to mistakes in GST filings. In this article, we will cover everything about invoice value—its meaning, components, legal basis, calculation, and significance under GST.
What is Invoice Value in GST?
In simple terms, invoice value in GST is the total amount payable by the buyer to the seller, which includes:
- The value of goods or services supplied (taxable value)
- Any additional charges linked to the supply (packing, freight, loading, insurance, etc.)
- The GST amount levied on the supply (CGST, SGST/UTGST, IGST, or Cess)
Formula:
Invoice Value = Taxable Value + Incidental Charges + GST
Legal Definition
- Section 15 of the CGST Act, 2017 – Defines the "value of supply" as the transaction value, i.e., the price actually paid or payable, provided supplier and recipient are not related and price is the sole consideration.
- Rule 46 of CGST Rules, 2017 – Specifies that the total amount including tax (i.e., invoice value) must be shown in the invoice.
Difference Between Taxable Value and Invoice Value
| Basis | Taxable Value | Invoice Value |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | Base price on which GST is calculated | Final amount payable including GST |
| Includes | Price of goods/services after discounts | Taxable value + Other charges + GST |
| Used For | GST calculation | Buyer payment, ITC, compliance |
| Example | Rs 1,00,000 | Rs 1,23,900 (after adding charges + GST) |
Fact: Many businesses wrongly assume that invoice value and taxable value are the same. But in GST, the taxable value is the base, while the invoice value is the final payable figure.
Components of Invoice Value in GST
A proper GST invoice (as per Rule 46 of CGST Rules) should contain the following details contributing to invoice value:
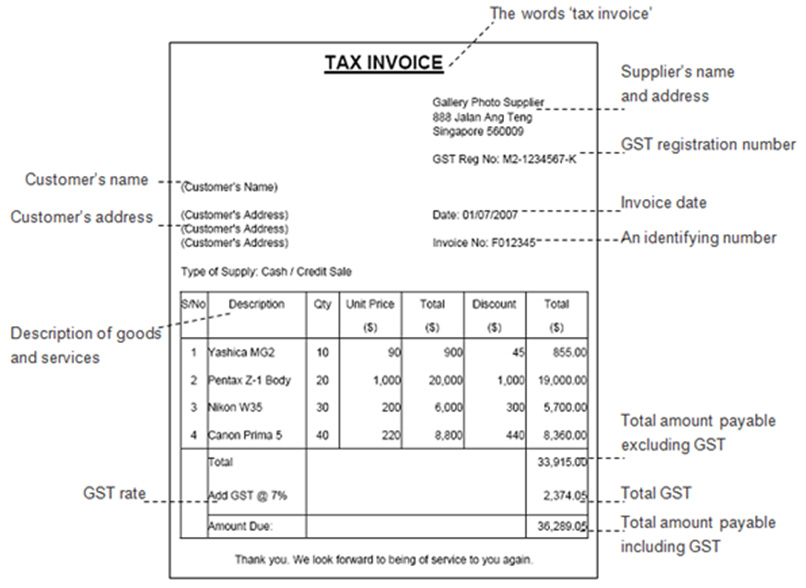
- Taxable Value – Base value of goods or services after adjusting discounts.
- Incidental Expenses – Any charges related to supply such as:
- Freight/transportation
- Packing and loading
- Insurance
- Handling charges
- Other Charges (if applicable) –
- Interest or late fees (if mentioned in invoice)
- Subsidies directly linked to price (except government subsidies)
- Taxes Applicable –
- CGST & SGST/UTGST (in intra-state supplies)
- IGST (in inter-state supplies)
- Compensation Cess (on luxury & sin goods like tobacco, coal, aerated water, etc.)
- Final Invoice Value – Sum of taxable value + additional charges + GST components.
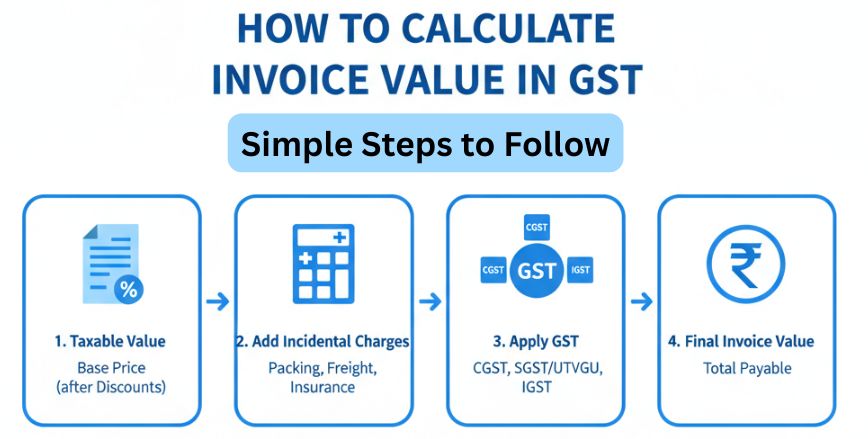
How to Calculate Invoice Value in GST
Calculating invoice value under GST involves adding up the taxable value, incidental charges, and the applicable GST. Here’s a step-by-step method:
Step 1: Determine the Taxable Value
Start with the base price of goods or services after deducting any eligible discounts.
- Example: Machinery price = Rs 5,00,000
Step 2: Add Incidental Charges
Include additional charges related to supply such as packing, freight, insurance, or loading.
- Packing charges = Rs 5,000
- Freight charges = Rs 10,000
- Total after charges = Rs 5,15,000
Step 3: Apply the Correct GST Rate
Calculate GST on the total taxable value (including incidental charges). The rate depends on whether it is an intra-state or inter-state supply.
- GST rate = 18% (CGST 9% + SGST 9%)
- GST amount = Rs 92,700
Step 4: Arrive at the Final Invoice Value
Add GST to the taxable amount (including charges) to arrive at the invoice value.
- Invoice Value = Rs 5,15,000 + Rs 92,700 = Rs 6,07,700
Invoice Value = Taxable Value + Incidental Charges + GST
This method ensures accuracy, helps avoid compliance errors, and makes GST filing smoother.
Treatment of Discounts in Invoice Value
As per Section 15 of the CGST Act, 2017:
- Pre-supply discounts (shown in invoice) → Deducted from taxable value.
- Post-supply discounts (given later) → Allowed only if:
- There is a prior agreement between buyer & seller.
- Buyer reverses proportionate ITC.
Example:
- Price per unit: Rs 1,000 × 100 units = Rs 1,00,000
- Discount @ 10% shown in invoice = Rs 10,000
- Taxable Value = Rs 90,000
- GST @ 18% = Rs 16,200
- Invoice Value = Rs 1,06,200
Why is Invoice Value Important in GST?
- GST Calculation – Determines exact tax liability.
- Input Tax Credit (ITC) – Buyers can claim ITC only if invoice value and tax details are correct.
- Compliance – Invoice value is reported in:
- GSTR-1 (Outward Supplies)
- GSTR-3B (Monthly return)
- E-invoicing system (if turnover exceeds threshold)
- Legal Documentation – Acts as proof of supply in audits and disputes.
- Transparency – Ensures clarity between buyer and seller regarding payment.
? Fact: According to CBIC, more than 70% of GST disputes arise due to incorrect invoicing and valuation.
Common Mistakes in Calculating Invoice Value
- Confusing taxable value with invoice value.
- Ignoring incidental charges (freight, insurance, etc.) in taxable base.
- Wrong treatment of discounts (not adjusting ITC properly).
- Incorrect application of IGST vs CGST/SGST.
- Not mentioning cess on applicable products.
FAQs on Invoice Value in GST
1. Does invoice value include GST?
Yes. Invoice value is the final payable amount that includes taxable value, incidental charges, and applicable GST.
2. Is invoice value and taxable value the same?
No. Taxable value is the base for GST, while invoice value is the taxable value + GST + other charges.
3. Which law defines invoice value in GST?
- Section 15 of CGST Act, 2017 (Valuation of Supply)
- Rule 46 of CGST Rules, 2017 (Invoice particulars)
4. Can invoice value be less than taxable value?
No. Invoice value is always greater than or equal to taxable value, as it includes GST and other charges.
5. How is invoice value shown in e-invoices?
In e-invoicing (mandatory for businesses above ?5 crore turnover in FY 2025), invoice value is auto-generated by the Invoice Registration Portal (IRP) after validation.
Conclusion
The invoice value under GST is not just a billing figure—it is the foundation of GST compliance. It determines how much tax is paid, how much ITC can be claimed, and whether a business stays compliant with GST rules.
By understanding the difference between taxable value and invoice value, applying correct GST valuation rules (Section 15), and ensuring invoices are error-free, businesses can avoid disputes and penalties.
In short, invoice value = transparency + compliance + credibility in GST.
